
The covalent radius of Cl 2 is half the distance between the two chlorine atoms in a single molecule of Cl 2. (d) This is a depiction of covalent versus van der Waals radii of chlorine. Vice Versa for anions since anions gain electrons to the outermost shell they usually will have bigger radii than their parent neutral atom. (c) The van der Waals atomic radius, r vdW, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms, such as argon, that are closely packed but not bonded. (b) The metallic atomic radius, r met, is half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a pure solid metal, such as aluminum. Lets see how this applies to a simple acid-base reaction between hydrochloric acid and fluoride ion: HCl +F HF + Cl (7.4.1) (7.4.1) H C l + F H F + C l. The pK a of the thiol group on the cysteine side chain, for example, is approximately 8.3, while the pK a for the hydroxyl on the serine side chain is on the. Recall that the driving force for a reaction is usually based on two factors: relative charge stability, and relative total bond energy. One of the reasons the periodic table is so useful is because its structure allows us to qualitatively determine how some properties of the elements vary versus their position on the periodic table.

use the general trends to predict the relative sizes of ions. describe the trend in ionic size for elements. describe the factors that determine the trend in ionic size.
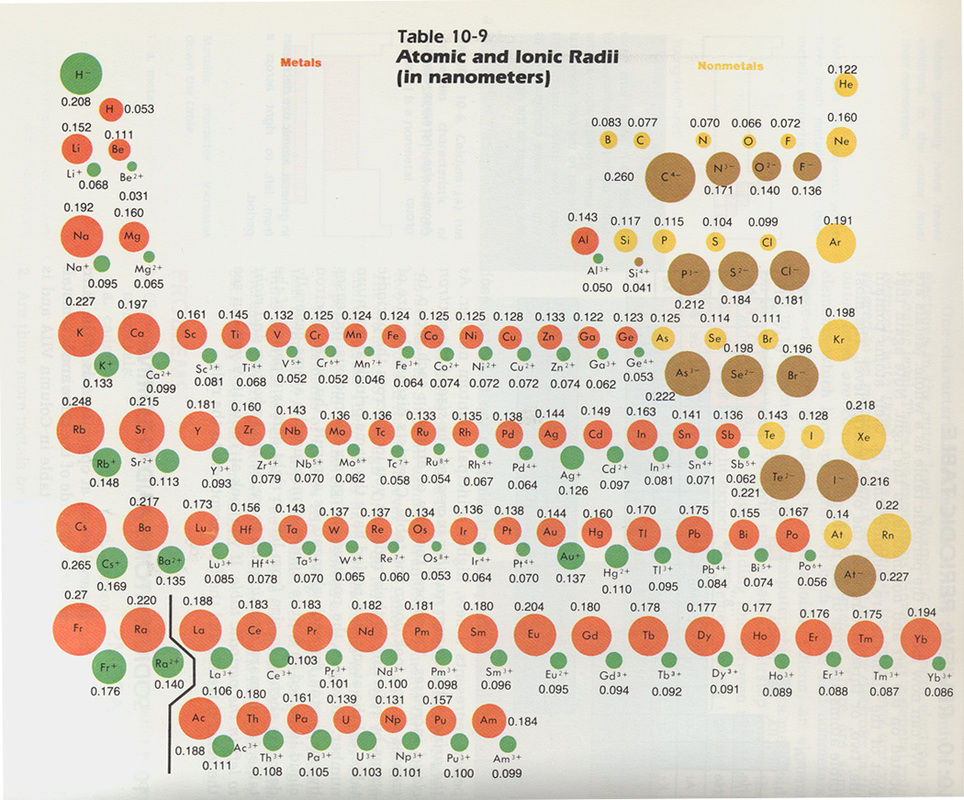
More importantly to the study of biological organic chemistry, this trend tells us that thiols are more acidic than alcohols. Learning Objectives Be able to state how certain properties of atoms vary based on their relative position on the periodic table. describe how cations and anions are formed. The general trend is that atomic sizes increase as.
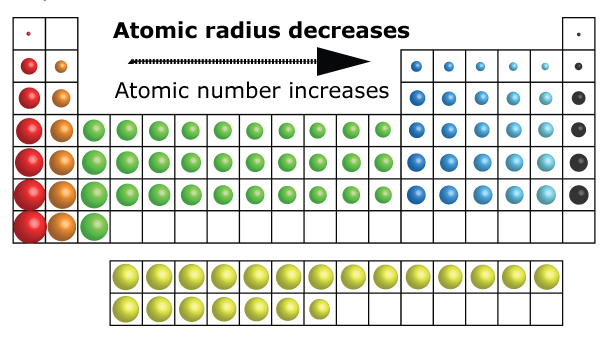
(a) The covalent atomic radius, r cov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as Cl 2. HI, with a pK a of about -9, is one the strongest acids known. Atomic radii represent the sizes of isolated, electrically-neutral atoms, unaffected by bonding topologies. Anions of a given element have a larger radius than the neutral atom, so I- will increase in. (b) The metallic atomic radius, r met, is half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a pure solid metal, such as aluminum.\): Definitions of the Atomic Radius. (viii) Iodine is a Group 17 element so its only ionic state is I-. When electrons are added to an atom to form an anion, the increased electron-electron repulsions cause the electrons to spread out more in space. Although there are some reversals in the trend (e.g., see Po in the bottom row), atoms generally get smaller as you go across the periodic table and larger as you go down any one column. Compare your predictions to the values given in model 1 below. (a) The covalent atomic radius, r cov, is half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms joined by a covalent bond in the same molecule, such as Cl 2. 1: Atomic Radii Trends on the Periodic Table. Predict the trend for the atomic radius for the elements in group I and group II of the periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
